Technical Integration Unit
Introduction
King Saud University has given the use of assistive technology in the educational process a tremendous priority . when it comes to students with disabilities, the necessity for these technologies are more pressing.
The advances in the field of assistive technologies customized to the needs of students with disabilities made it possible for them to expand their comprehension potential. Assistive technology applications, software, and devices that facilitate access to learning resources is a significant aspect to create and/ or rehabilitate the educational environment for student with special needs as well as facilitating their access to the electronic services provided by university.
Below is a list of devices and software categorized by the types of disability they assist:
First: assistive devices and software for students with visual impairment
King Saud University provides a range of software and hardware catering to visually impaired students for a direct access to its resources in libraries and information centers.
Software

JAWS: Job Access With Speech, is the world's most popular screen reader (emerged with Windows 95), developed for computer users whose vision loss prevents them from seeing screen content or navigating with a mouse. JAWS provides speech and Braille output for the most popular computer applications such as Access5, Word, and Excel. Version 6.0 supports Arabic langue.

HAL: Hal Screen Reader is a voice output screen reader program designed for use by individuals who are blind or have low vision. It helps them to peruse their education, work or even everyday live activates that involve using PCs Hal will talk you through its automatic and user friendly installation. Hal's sophisticated technology makes all kinds of Windows applications, the Internet and email, easy to use. Hal works by recognizing and reading information from the computer screen aloud through your computer's soundcard. Screen information is also displayed in Braille for users of the many supported Braille devices. The information provided is comprehensive: Hal not only reads text but also recognizes Windows dialogs, icons, buttons, menus and controls.
Zoomtext: It enlarges and enhances everything on a computer screen, making all applications easy to see and use. It displays crystal clear text and pictures at all magnification levels reducing the hustle of accessing information for those with low vision.
Hardware

Braille Display: Text on a computer can be displayed in braille on a braille display. This is a device that has a row of plastic or metal pins. The pins are controlled by a computer and move up or down to display the characters on a computer screen in braille.

braille display and notetaker: The device works as a laptop computer for blind and visually impaired, enabling them to accomplish variety tasks to keep up their various needs at work, study or reading environments. The most important tasks this device helps with are; writing, conservation, connecting to the Internet and browsing. It provides elicit information through producing Braille lines or listening through loudspeaker. The users then retrieve and safe the information they need.

Braille embosser/ printer: A braille embosser is an impact printer that renders text(in a doc. format) as tactile braille cells. Using braille translation software, a document can be embossed with relative ease, making braille production efficient. Many libraries provide these printers to visually impaired students so they can archive the materials they read or listen to for future personal usage.
Second: assistive devices and software for student with hearing impairment
King Saud University provides a range of software and hardware catering to students with hearing impairment allowing them to access to its resources in libraries and information centers.
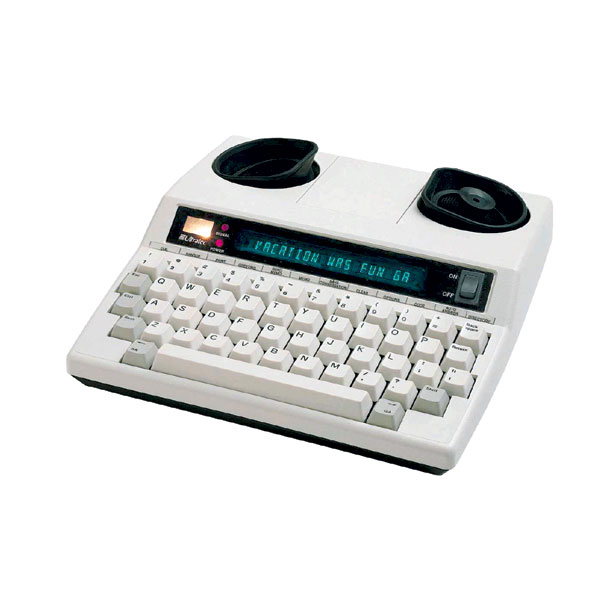

ultratec supercom 4400 tty: this device is used to printout audio phone calls and messages.

Frequency- modulated (FM): is an assistive listening devices system that makes it easier for people with hearing loss to hear what others are saying in noisy environments, like closed building. This wireless system, also called a personal FM system, uses radio waves to deliver speech signals directly from the speaker's mouth to the listener's ears. The person speaking, like a teacher, wears the microphone portion of the FM system. This microphone encodes their voice into a frequency-modulated signal. Being a wireless system allows students to freely move from on classroom to another with string attached.
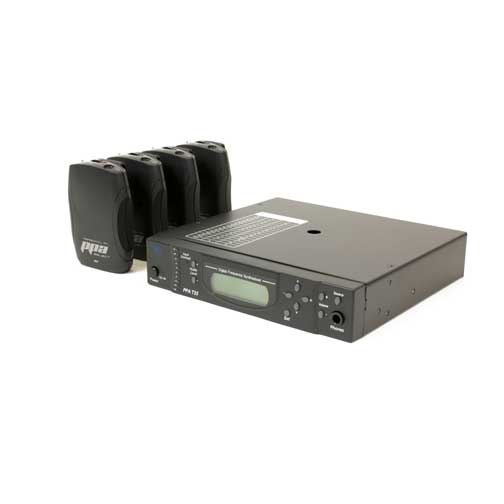

Audio loops: A hearing loop consists of a physical loop of cable or an array of looped of cables which are placed around a designated area, usually a room or a building. The cable generates a magnetic field throughout the looped space which can be picked up by a hearing aid, cochlear implant (CI) processors, and specialized hand-held hearing loop receivers for individuals without telecoil compatible hearing aids.
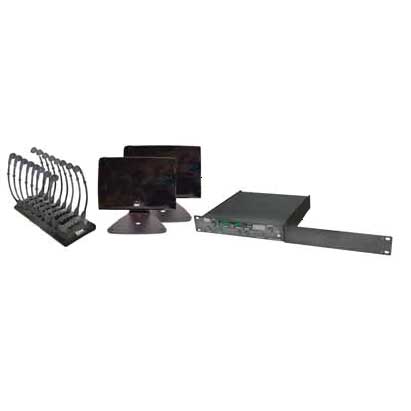

Infrared system: this system is used in places where hearing impaired individuals need to move freely as in a theater or a library. It uses invisible light beams to carry sound from the source to a personal receiver. (The sound source must be in the line of sight.) Different types of attachments may be connected to the personal receiver such as a neckloop or a behind-the-ear silhouette inductor. The telecoil then picks up sound from the receiver via the attachment.
Accomplishments
- Conducting a CDL course for students with visual impairment.
- Collaborating with the International Computer Driving License - ICDL in developing CDL tests.
- Developing students with special needs laboratories.
- Establishing students with special needs laboratories at the Preparatory Year.
- Participating in KSU events aimed at students with special needs.
- Conducting a study on the technical integration of KSU'S ATMs accessibility.
- Conducting a study on the technical integration of King Salman Library accessibility.
- Communicating with KSU's students with special needs via social network applications.
- Establishing AUP website.
- Running awareness programs for web accessibility.
Future projects
- Developing electronic services at AUP website.
- Activating the Web Accessibility project in all KSU websites.
- Equipping KSU laboratories with Assistive technology applications, software, and devices geared towards students with special needs.
- Providing technical support for ICDL courses in KSU laps.
- Integrating courses materials for students with special needs.
- Conducting filed studies to evaluate and improve electronic services provided by KSU to students with special needs.
Technical Integration unit executive plan
- Integrating courses materials for students with special needs.
- Sinning a bilateral agreement with Deanship of e-Learning & Distance Learning.
- Setting parameters targeting publishing students with special needs' electronic courses.
- Establishing electronic courses policy at KSU.
- Providing technical support to students with special needs.
- Activating the Web Accessibility project in all KSU websites
- Sinning a bilateral agreement with Deanship of e-Transactions & Communications.
- Rising awareness about Web Accessibility notion and its terminology.
- Conducting workshops, seminars, and lecture on the subject of Web Accessibility.
- Publishing a guidebook on Web Accessibility parameters.
- Establishing Web Accessibility policy at KSU.
- Equipping KSU laboratories with Assistive technology applications, software, and devices geared towards students with special needs
- Assisting colleges with identifying its need for the software and hardware required.
- Providing technical consultation about the software and devices.
- Providing technical consultation on software for students disabilities.
- Providing technical consultation for colleges in regards to their websites and electronic services.
- Conducting filed studies to evaluate and improve electronic services provided by KSU to students with special needs
- Locate areas of study.
- Allocate international benchmarks in similar research centers.
- Publish scientific studies on the field of Assistive technology applications for individuals with special needs.
